Tire vulcanization is a reliable method for repairing tire damage. Experts say that using vulcanized rubber for combination repairs is safe and effective. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) also endorses this method. Vulcanized rubber forms a strong seal, preventing leaks and future problems. Some people believe that retreaded or repaired tires are less safe than new tires. However, studies show that retreaded tires are just as safe as new tires. This applies even to buses and emergency vehicles. Numerous studies have shown that, when done correctly, tire vulcanization can provide a strong and durable repair.
Key Takeaways
- Vulcanization is an effective method for repairing tire damage. It works well to repair punctures caused by nails or sharp objects. Professional vulcanization repairs can extend the life of a tire by 7 to 10 years. This is a smart and cost-effective method. Some tire damage is irreparable. If the sidewall is damaged or the puncture is larger than 6 mm, you will need to replace the tire for safety. After repair, check the tire frequently to ensure it is safe. Check the tire for leaks or other problems. Always have vulcanization done by a professional mechanic. This will ensure a strong and safe repair.
How vulcanizing a tire works

The vulcanizing process
Tire vulcanization utilizes high temperatures, high pressures, and special chemicals. These factors help repair damaged rubber and enhance its strength. Charles Goodyear pioneered this process in 1839. He found a way to make rubber tough and resilient. Over the years, experts have continuously improved the vulcanization process. This helps extend the life of tires and ensure their safety. Today’s tires use both natural and synthetic rubber. They also contain steel and other high-strength materials to improve grip and safety.
During vulcanization, the rubber undergoes significant changes:
- The rubber transforms from a simple shape into a robust network structure.
- Sulfur mixes with the rubber, forming sulfur bridges.
- The tire becomes stronger and has greater resistance to wear, heat, and chemical corrosion.
These changes allow the tire to maintain good performance every day. Vulcanization is a method of repairing a tire by connecting new rubber to the damaged areas. This method enhances the strength of the repair and prevents tire leaks.
Tip: The best results from vulcanization depend on skilled workers using appropriate tools and adhering to safety rules.
What damage can be fixed
Vulcanization can repair a variety of tire damage, but not all. It is primarily used to repair holes in the tire tread. This method is suitable for deep cuts or holes caused by nails or sharp objects. Vulcanization seals the hole, restoring the tire’s strength.
The table below shows the types of damage that vulcanization can repair:
| Tire Damage Type | Repair Method | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Cuts | Vulcanization | High |
| Sidewall Damage | Not Recommended | Low |
Most experts advise against repairing sidewall damage. The sidewall has a significant range of bending and movement, so repairs are usually not long-lasting. This can be dangerous, especially at high speeds. For holes in the tire tread, vulcanization is an effective and durable repair method.
Effectiveness and safety of vulcanizing
Vulcanizing Durability of repairs
Tire vulcanization creates a strong bond between the patch and the rubber. This helps the tire regain most of its original strength. Many people wonder how long a repaired tire will last. Professional tire repair techniques can extend tire lifespan. If done properly, a patch on the tread can last 7 to 10 years. This applies to normal driving conditions. For those looking to extend tire life, vulcanization is a good option.
| Aspect | Professional Patch Repair | No Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan Extension | 7 to 10 years possible | Tire remains unusable without repair or replacement |
A good repair prevents leaks. It ensures tire safety during daily driving. Vulcanization also protects against high temperatures and wear, common causes of tire damage. Many tire shops use this method because it effectively repairs punctures in the tread for a long time.
Safety after vulcanizing
Safety is paramount when repairing tires. Vulcanization restores most of the tire’s original shape and strength, making it suitable for most driving scenarios, even highways. Insurance companies recognize the value of professional repairs and often insure shops that offer vulcanization and other tire services.
| Insurance Type | Description |
|---|---|
| General Liability | Covers claims for personal injury or property damage resulting from tire repair. |
| Property Insurance | Insures against damage to shop property, including vulcanizing equipment. |
| Workers’ Compensation | Provides coverage for employees injured during tire repair (including vulcanizing). |
- Appropriate insurance can cover losses caused by vulcanizing tire repair.
- It helps prevent business losses due to liability claims.
This is crucial for shops that provide vulcanizing and other repair services.
Laws and regulations are also essential for tire repair safety. Different regions have different regulations regarding vulcanization. For example, the UK uses BS AU 159G to set tire repair standards. In the US, the Department of Transport sets the rules, but individual states have their own laws.
| Regulation | Description |
|---|---|
| BS AU 159G | Governs repair of tires for vehicles on public highways in the UK, including inspection steps. |
| U.S. DOT Guidelines | Sets general guidelines for tire repairs, with state-level enforcement. |
- Many countries do not allow retreaded tires to be repaired more than once.
- Some tire damage cannot be repaired by law.
- Always check local regulations to ensure compliance.
Tire repairs are safe and secure if vulcanized by a trained worker. Complying with the law and purchasing appropriate insurance protects drivers and repair shops.
When to Vulcanizing or replace

Best cases for vulcanizing
Vulcanized tires can effectively repair certain damage. Tire shops use vulcanization when the tread is punctured. If a nail or other sharp object punctures the tread, vulcanization can repair it. This repair method restores the tire’s strength, ensuring safe daily driving.
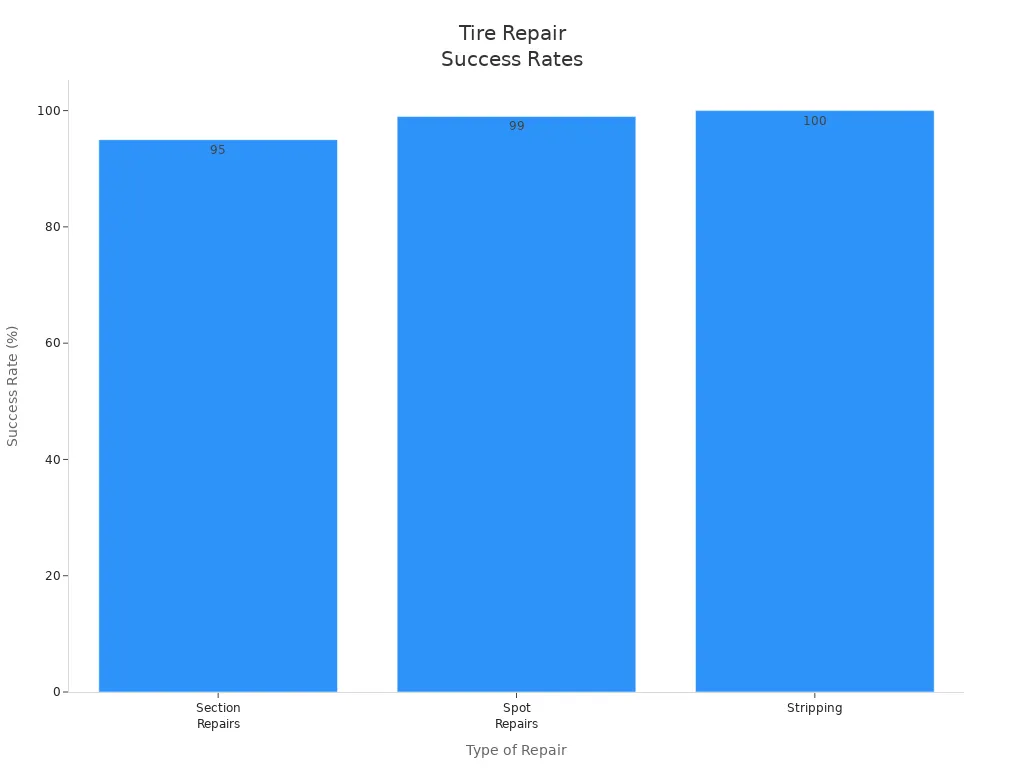
Tire manufacturers state that vulcanization is suitable for certain specific repair situations. The table below lists tire repair types, repair scope, and repair results:
| Type of Repair | Description | Success Rate | Application Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section Repairs | For bad damage, like cuts through tire cords. | ~95% | Not for heavy loads. |
| Spot Repairs | For outside damage, like sidewall cuts and bead damage. | >99% | Good for any use. |
| Stripping | For thin inner lining showing cords, new rubber goes inside. | ~100% | Works well for farm tires. |
Partial repair is the most effective. It can repair small holes that haven’t damaged the cords. Partial repair can repair deeper cuts, but is not suitable for large trucks or buses. Strip repair is suitable for situations where the inner liner is too thin, mainly seen in agricultural tires.
Tires with holes smaller than 6 mm in the tread can be vulcanized. Vulcanized repair can seal the hole and extend tire life. Many people choose vulcanized repair to avoid buying new tires after a blowout.
Note: Always have a trained professional inspect the tire first. They will know whether vulcanized repair is the safest repair method.
When replacement is needed
Sometimes, repairing a tire is not safe. Some damage means that even vulcanized repair cannot fix the tire. If a driver notices the following warning signs, the tires should be replaced:
- Sidewall damage
- Large punctures (diameter greater than 6 mm)
- Tread wear
- Internal cord damage
- Thinned tread
- Large cuts
- Unrepaired old damage
Tires with sidewall damage or large cuts cannot be repaired. During driving, the sidewall will bend significantly. Repairs in this area are not durable and may quickly fail. If the tread is thin or the cords are damaged, the tire’s strength is insufficient. Vulcanized repairs cannot restore its safety.
If a large puncture or a puncture near the sidewall appears after a blowout, it should not be repaired. Replacing the tires is the safest option for everyone. Worn treads mean the tire will not have effective grip even after repair.
Tip: Regularly check your tires for damage. Early detection can prevent blowouts and ensure your safety.
Vulcanizing Tire repair methods compared
Vulcanizing vs. plugs and patches
There are many ways people repair tires. Vulcanization, patch repair, and surface mount repair are all common options. Each method has its advantages. Vulcanization forms a strong bond inside the tire. It uses high temperatures and chemicals to enhance the repair. Plugs seal holes from the inside of the tire. Plugs are best for small holes far from the sidewall. Patches cover holes on the liner. Patches are better for larger or irregularly shaped holes.
The table below compares these methods:
| Method | How It Works | Best Use Case | Longevity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plug | Seals hole from inside | Small punctures in tread | Several years |
| Patch | Bonds to inner liner | Larger or irregular punctures | Lasts tire’s lifetime |
| Vulcanizing | Heat/chemicals create strong bond | Most tread repairs | Lasts tire’s lifetime |
Safety rules from the American Tire Manufacturers Association and the Tire Industry Association help guide repair work. The location and size of the hole are crucial. Plugs may not last as long as patches or vulcanization. Patches and vulcanization generally improve tire safety and reliability.
SUNSOUL Tire Patch overview
SUNSOUL tire patches are widely popular in tire repair shops. Many car owners and repair shops trust the brand’s quality. SUNSOUL produces over two million patches monthly, meaning there are always fresh patches available. These patches use vulcanized rubber for strong adhesion, making repairs easy and convenient, and effectively preventing leaks. User feedback indicates that these patches are easy to use regardless of the size of the puncture. The kit offers excellent value and remarkable results.
SUNSOUL sells a variety of products, including chemically cured tire patches, dual-cured tire patches, rubber solutions, and tire installation pastes. Each product is suitable for different vehicle types and repair needs.
| Vehicle Type | Repair Scenario |
|---|---|
| Passenger Cars | Quick Highway Patching of Tires |
| Commercial Vehicles | Durable Seals for All Tire Types |
| Off-road Vehicles | Emergency repairs on trails |
| Urban Commuters | Reliable fixes for city driving |
SUNSOUL uses advanced materials. These patches remain flexible in a temperature range of -40°F to 250°F, meaning they function well in both hot and cold weather. Each tire patch undergoes strength and safety testing, with an adhesion strength exceeding industry standards, ensuring it won’t detach even under heavy loads. Brands like SUNSOUL offer peace of mind when repairing tires.
Note: SUNSOUL provides dealers with a stable supply, reasonable prices, and training to ensure optimal repair results for every tire.
Vulcanizing Limitations and concerns
Sidewall and cold weather risks
Tire repair has limitations. Experts warn against repairing sidewall damage. The tire sidewall is more prone to bending and deformation than the tread, and it experiences greater stress with each vehicle’s movement. Attempting to repair a puncture in the sidewall may result in an insufficient bond, increasing the risk of leaks and tread detachment. In the worst-case scenario, the tire could even blow out while driving.
| Risk | What Happens |
|---|---|
| Weak repair bond | Patch may detach |
| Air leaks | Rapid tire leaks |
| Tread separation | Tread may peel off the tire |
| Blowouts | The tire may blow out while driving |
Cold weather can also affect tire repairs. Low temperatures harden rubber. Hardened tires are less flexible, so patches or repairs may not adhere properly. Drivers should check their tires more frequently in winter. If a blowout occurs in cold weather, have it checked by a professional before a long trip.
Tip: Never attempt to repair a sidewall puncture. For safety, always replace the tire with a damaged sidewall.
Long-term safety
Long-term safety depends on good repairs and regular maintenance. Repaired tires require regular inspection. Drivers should pay attention to for leaks, bulges, or changes in tire feel. Monthly checks help detect problems early. Keeping records of repairs and inspections helps track tire condition.
| Maintenance Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Daily Maintenance Checks | Develop a regular tire inspection and maintenance plan. |
| Record Maintenance Activities | Record all repairs and inspections. |
| Work with Qualified Technicians | Only allow trained personnel to repair or inspect tires. |
Tires that are properly maintained after repair can last a long time. However, if a tire continues to leak air or develops new damage, it is safer to replace it. Tires also impact the environment. Approximately 3 billion new tires are produced each year, of which 800 million end up as waste. Tire wear releases microplastics, which pollute oceans and rivers.
Note: Good maintenance and safe driving help extend tire life and protect the environment.
Recent research shows that vulcanized tire repair helps extend tire life. This can save money for truck and bus drivers. Experts point out that the following points are important:
- Vulcanized tires are cheaper and help drivers get back on the road faster.
- Only professional mechanics should inspect and repair tires.
- Repairing tires is best done to small holes in the tread.
Drivers should remove tires for a thorough inspection. If unsure, consult a professional. This ensures safe driving every time.
FAQ
How long do vulcanized tire repairs last?
Vulcanized tire repairs can last for many years. If repaired by an experienced mechanic, the repair effect is usually comparable to the lifespan of the tire itself. Regular checks help ensure tire safety during daily driving.
Can anyone repair a vulcanized tire themselves?
Most people should not attempt to repair vulcanized tires themselves. This process requires specialized tools and training. For safety and quality, repairs should be performed by professionals.
When should a punctured tire be replaced instead of repaired?
If the tire sidewall is damaged, the puncture is too large, or the tread is severely worn, the punctured tire should be replaced. These issues make repairs unsafe.
Is vulcanization suitable for all types of vehicles?
Vulcanization is suitable for passenger cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural equipment. The repair effect can remain good under normal driving conditions. Always check the tire type and follow expert advice.
What is the difference between a patch and a plug?
A patch covers the inside of the tire, sealing the puncture. A plug fills the puncture from the outside. Vulcanized tires typically use patch pads for a stronger and more durable repair.






